
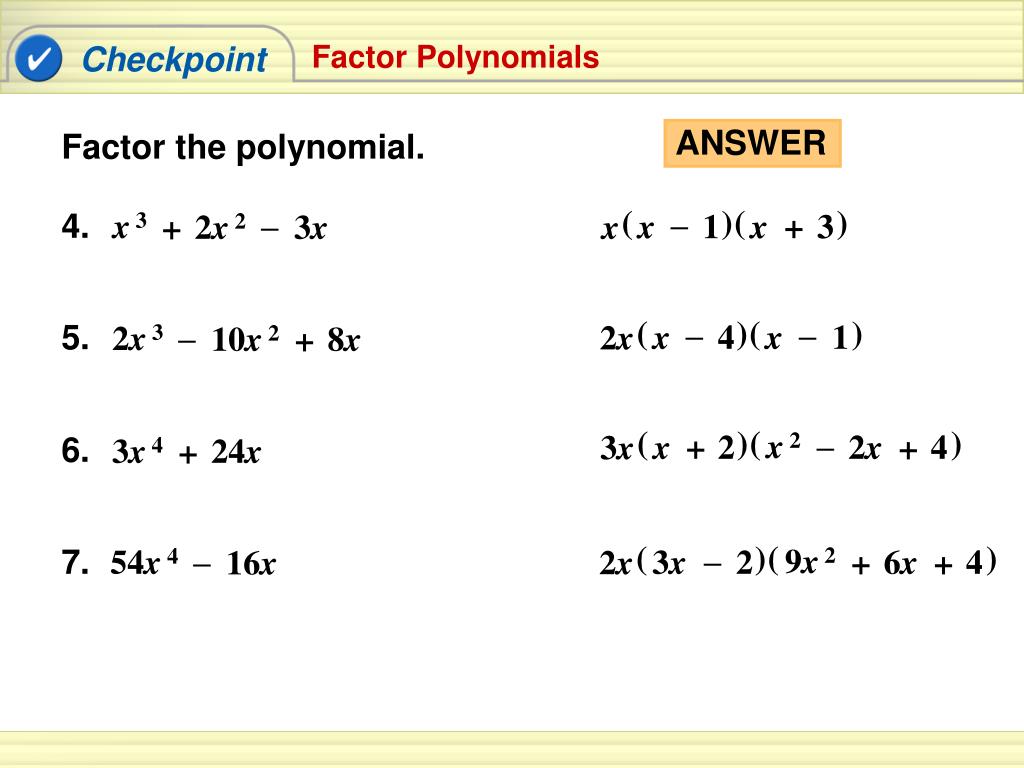
Factoring By Grouping Factoring By Grouping X^3
About Transcript Factoring higher degree polynomials involves breaking down complex expressions into simpler parts. This process includes identifying common factors, using the distributive property, and recognizing perfect squares.

Factoring a Cubic Polynomial Algebra I YouTube
This algebra 2 and precalculus video tutorial explains how to factor cubic polynomials by factoring by grouping method or by listing the possible rational zeros of the polynomial and then.

How To Factor A Cubic Polynomial How to Factor a Cubic Polynomial 12 Steps (with Pictures
Factoring by Grouping This is by far the nicest method of the two, but it only works in some cases. Consider the polynomial p(x) = x3 4x2 + 3x 12: We group the rst two terms and the last two terms together: p(x) = (x3 4x2) + (3x 12) and then we pull out the common factors: p(x) = x2(x 4) + 3(x 4): Notice now that these two terms now have x

How to Factor a Cubic Polynomial 12 Steps (with Pictures)
Factoring Cubic Polynomials Robert G. Underwood 1. Introduction There are at least two ways in which using the famous Cardano formulas (1545) to factor cubic polynomials present more difficul-ties than the quadratic formula poses when factoring quadratic polynomials. First and obviously, with its cube roots and roots of

Factoring Polynomials Khan Academy Example 3 Factoring quadratics by taking a common factor
A tutorial on how to factorise polynomials of degree 3 (cubic functions). This video will cover the more popular of the two methods: the "kx" method.

i is a number Factoring Flow Chart for Quadratic and Cubic Polynomials Math school, High
To find the factored form of a polynomial, this calculator employs the following methods: 1. Factoring GCF, 2 Factoring by grouping, 3 Using the difference of squares, and 4 Factoring Quadratic Polynomials Method 1 : Factoring GCF Example 01: Factor 3ab3 −6a2b 3ab3 −6a2b = 3 ⋅a ⋅b ⋅b ⋅ b−2 ⋅ 3 ⋅a ⋅ a⋅ b = = 3ab(b2 −2a) solve using calculator
How To Factor A Cubic Polynomial Given That X 5 Is A Factor Of The Cubic Polynomial P X X3 3
The goal of this free guide on how to factor polynomials is to give you plenty of step-by-step practice with factoring polynomials—including polynomials with 4 terms (cubic polynomials)—so that can become more comfortable with factoring all kinds of polynomials.
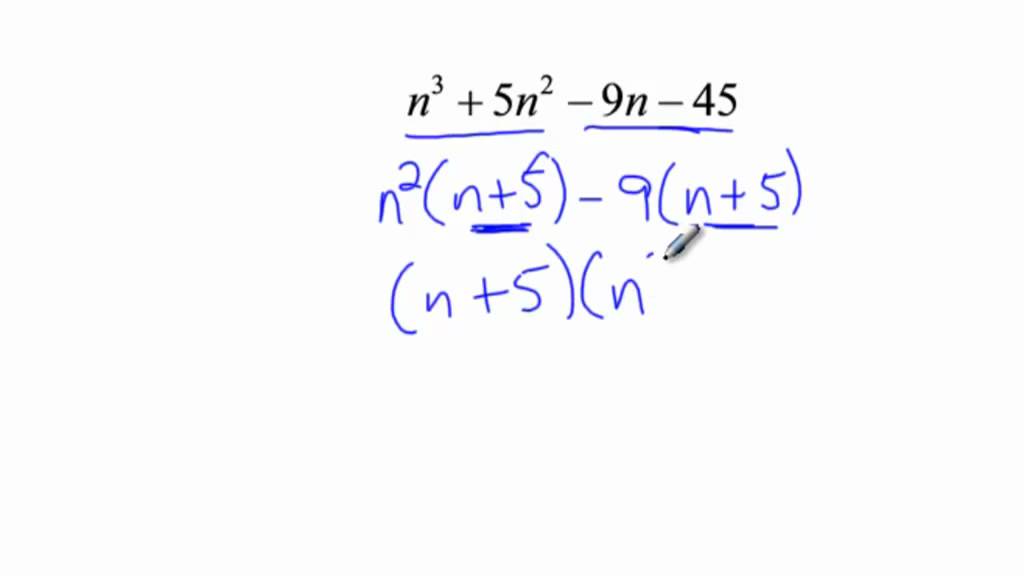
How To Factor Cubic Polynomials How to Solve Equations that are Not Perfectly Cubed Video
7 Answers Sorted by: 11 By the Rational Zero Theorem all the rational roots of x3 − 12x + 9 x 3 − 12 x + 9 must have a numerator which is a factor of 9 9 and a denominator which is a factor of 1 1. Therefore they have to be of the form 9 1 = 9 9 1 = 9 or 3 1 = 3 3 1 = 3. Let f(x) =x3 − 12x + 9 f ( x) = x 3 − 12 x + 9.
PPT 6.5 Factoring Cubic Polynomials PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2795627
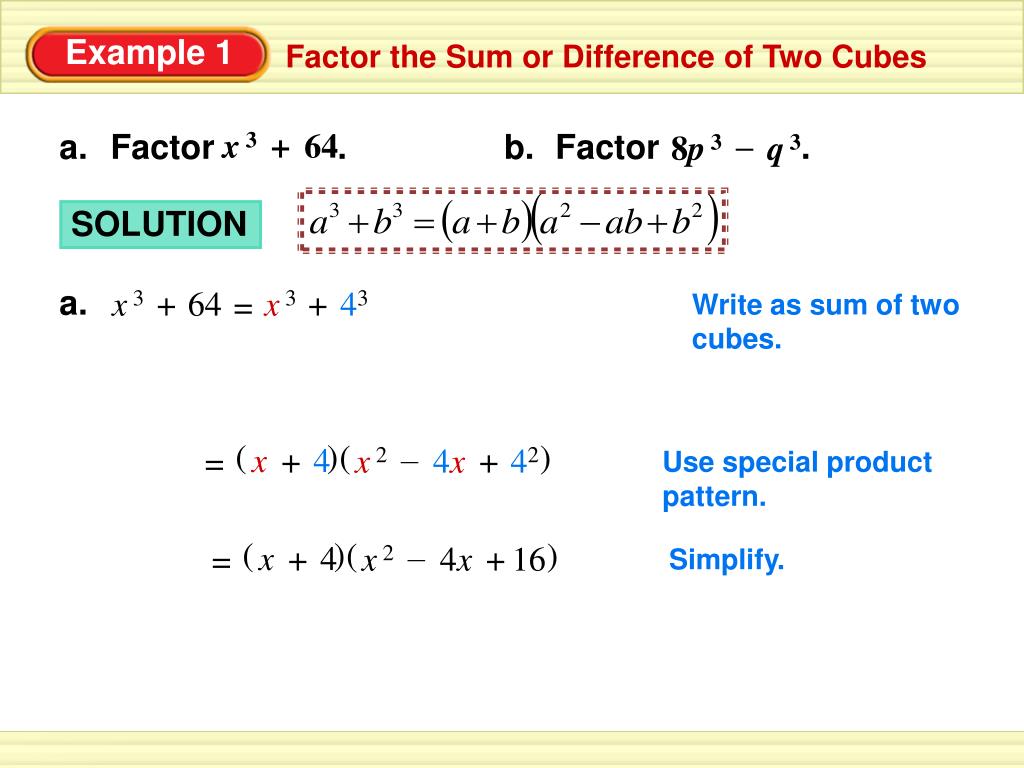
Factoring is nothing but breaking down a number or a polynomial into a product of its factor which when multiplied together gives the original. Factoring Formula for sum/difference of two nth powers are, Product Formulas \ [\large a^ {2}−b^ {2}= (a−b) (a+b)\] \ [\large a^ {3}−b^ {3}= (a−b) (a^ {2}+ab+b^ {2})\]

How to Factor a Cubic Polynomial 12 Steps (with Pictures)
Factoring a Cubic Polynomial - Algebra I BroandSisMathClub 18.4K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 4.8K views 8 years ago In this video, you will learn how to factor a cubic polynomial. A.
.PNG)
Factoring Cubic Trinomials 24 best images about Binomial & Trinomial on Pinterest Montessori
Whenever you factor a polynomial (cubic or otherwise), you are finding simpler polynomials whose product equals the original polynomial. Each of these simpler polynomials is considered a factor of the original polynomial. For example, the binomial x ² - 100 has two factors (x + 10) and (x-10). Why?

Algebra II Ch55 Part B Factoring Cubic Polynomials YouTube
The three methods we use for factoring a cubic polynomial are splitting terms using the ad-method, finding a factor by applying the rational root theorem, and cubic formulas for sum, difference, etc. Jump to Questions Irreducible Polynomials Polynomials like 2x + 1 or 3x 2 − x + 1 cannot be factorized. These are irreducible polynomials.
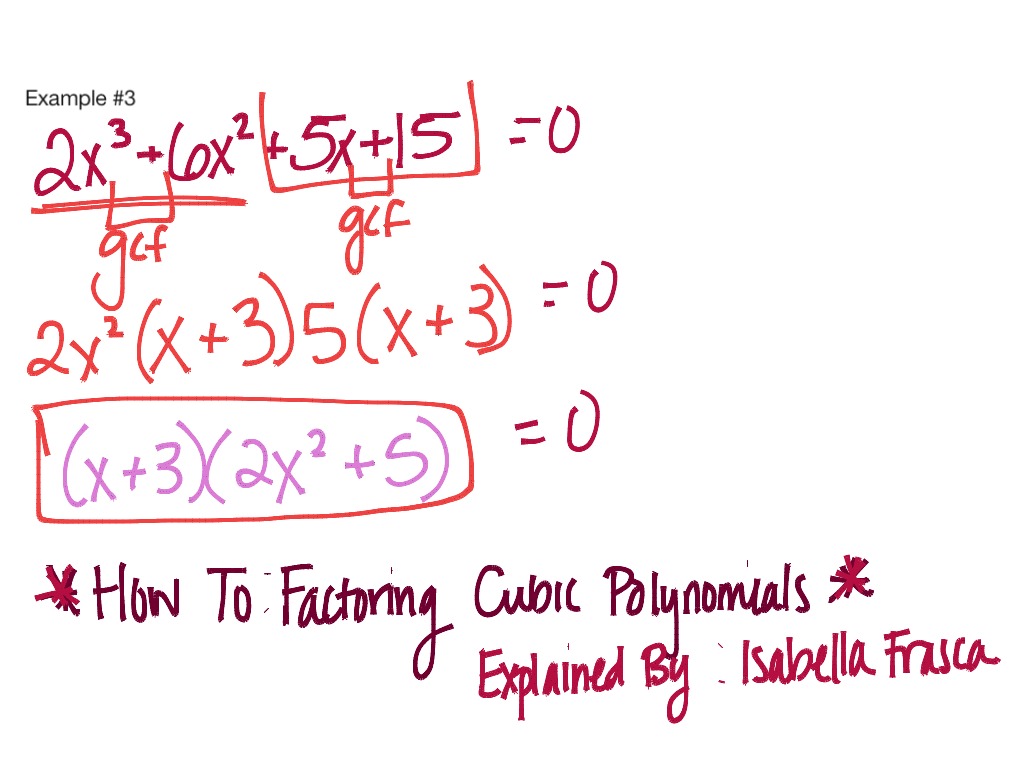
Factoring Cubic Polynomials Math, Algebra 2 ShowMe
Factoring difference of cubes (video) | Khan Academy Algebra (all content) Course: Algebra (all content) > Unit 10 Factoring difference of cubes Math > Algebra (all content) > Polynomial expressions, equations, & functions > Advanced polynomial factorization methods © 2024 Khan Academy Terms of use Privacy Policy Cookie Notice
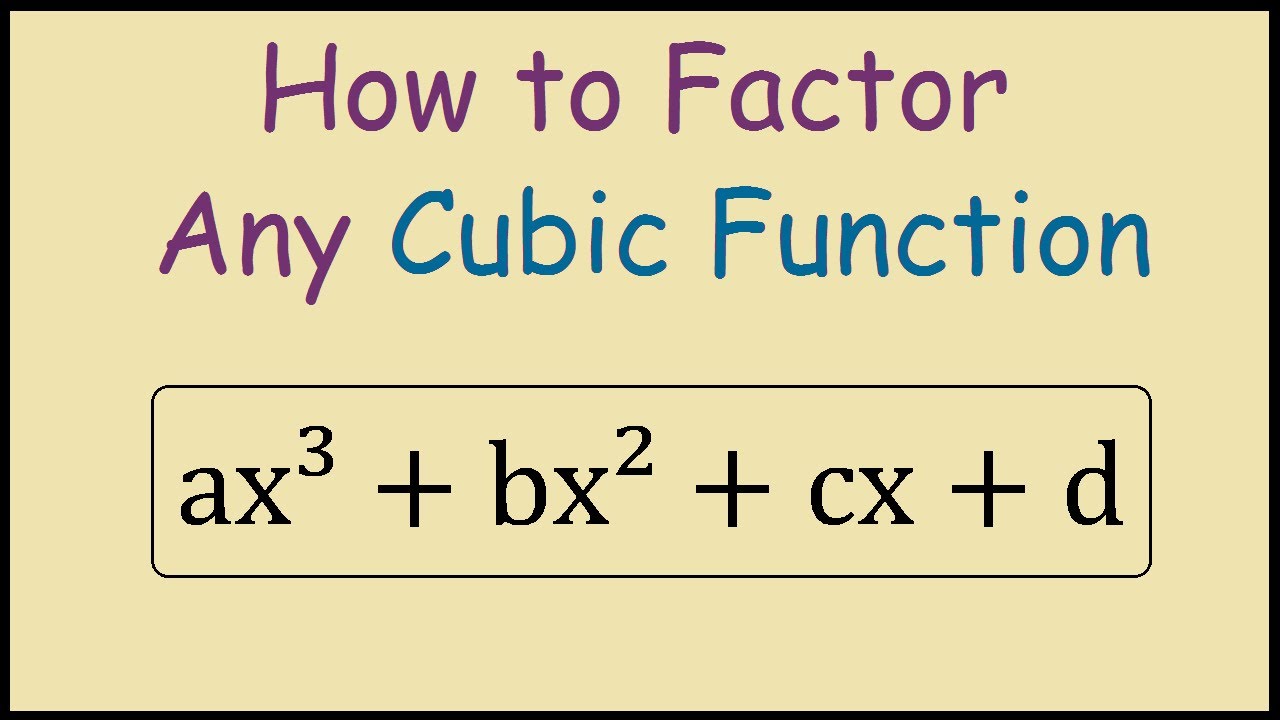
How to factor a cubic function YouTube
Every cubic polynomial will have 3 factors. To find those factors, we follow the following steps. Step 1 : We can find one linear factor of the given cubic polynomial using synthetic division. Step 2 : At the end of the first step, we will have quadratic factors. By factoring the quadratic equation, we can get other two factors.

Factor Solve These Cubic Equations In Less Than A Minute Otosection
1 Group the polynomial into two sections. Grouping the polynomial into two sections will let you attack each section individually. [1] Say we're working with the polynomial x 3 + 3x 2 - 6x - 18 = 0. Let's group it into (x 3 + 3x 2) and (- 6x - 18) 2 Find what's the common in each section. Looking at (x 3 + 3x 2 ), we can see that x 2 is common.

How to Factor a Cubic Polynomial 12 Steps (with Pictures)
If you are factoring a polynomial and run into an irreducible quadratic, just leave it alone. The irreducible quadratic would be considered one of the factors of the polynomial. Factoring Cubic Functions.. Example \(\PageIndex{12}\): Factoring a Cubic Function. Completely factor the function \(f(x)=x^3+8x^2+21x+18\).